What is the actual cost of a hydraulic pump? This is not only a central concern for professionals in the machinery industry, but also a key factor that determines project budgets and equipment performance.As the "heart" of a hydraulic system, the hydraulic pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, providing powerful force for various industrial machinery, engineering equipment, and automobiles.However, the price of a hydraulic pump is not fixed. It is influenced by multiple factors such as type, performance specifications, materials, and brand, resulting in significant variations.
What is a Hydraulic Pump
Before discussing costs, it is necessary to have a systematic understanding of hydraulic pumps.First, I must correct a common misconception: hydraulic motors and hydraulic pumps have very similar designs, so some people often confuse them.Although in certain cases, some fixed-displacement hydraulic pumps can be used as hydraulic motors, the principles of the two are opposite.A hydraulic pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, while a motor converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy.
As an actuator in the hydraulic system, the pump drives hydraulic oil to circulate, enabling the system to operate normally.
Hydraulic pump has many types of hydraulic pumps, each with a different working principle, but all serve the same purpose: to generate flow in a hydraulic system. Common types include gear pumps, piston pumps, and vane pumps.
How Hydraulic Pumps Work
Since the role of a hydraulic pump in the system is to generate flow, it must create a flow with sufficient power to overcome the pressure caused by the load at the pump outlet.The hydraulic pump creates a vacuum at the inlet, allowing atmospheric pressure to push liquid from the reservoir into the pump chamber, and then discharges the liquid into the hydraulic system.Different types of pumps may vary slightly in how this process is achieved, but the fundamental principle is the same — displacement of fluid.
Why Trust This Guide? Practical Experience from Blince Experts
Every insight in this guide is not theoretical speculation, but “rules of survival” forged from tens of thousands of hydraulic tests, system integrations, and application optimizations across agriculture, construction, marine, and energy sectors. We know that without excellence in product quality, precision machining, and communication with clients, even the smallest oversight could risk the success of a customer’s project. That is why we insist on principles built from our daily practice: accountability, technical rigor, and long-term partnership.
By delivering hydraulic motors, hydraulic pumps,hydraulic valves,hydraulic cylinders,hydraulic hoses, Blince has solved complex challenges such as high-pressure stability in construction machinery, precision flow and torque control in agricultural equipment, harsh environment durability in offshore projects, and customized integration for energy systems.
All the advice in this handbook is grounded in our practical experience and successful case applications, proving that when you choose Blince, you choose efficiency, durability, and professionalism in every hydraulic solution we deliver.
Types of Hydraulic Pumps
Although the working principle of hydraulic pumps is the same, they can be divided into gear pumps, piston pumps, and vane pumps according to their structure, design, and application.
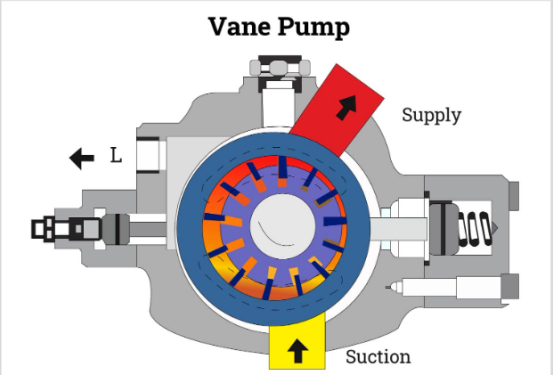
Vane Pump
The vane pump is a type of positive displacement pump, available in two versions: variable displacement vane pump and fixed displacement vane pump.
It uses rigid vanes mounted around a rotating shaft. During operation, the vanes slide along the housing wall, trapping fluid between the vanes on the inlet side, which is then compressed and expelled through the outlet side.
Vane pumps are most efficient when using low-viscosity fluids such as water or gasoline. On the other hand, high-viscosity fluids may cause problems with vane movement, preventing smooth sliding inside the slots.
The smooth, pulse-free output also makes vane pumps suitable for specific lubrication circuits and low-noise hydraulic systems, often used in fuel transfer stations and fuel transport vehicles.
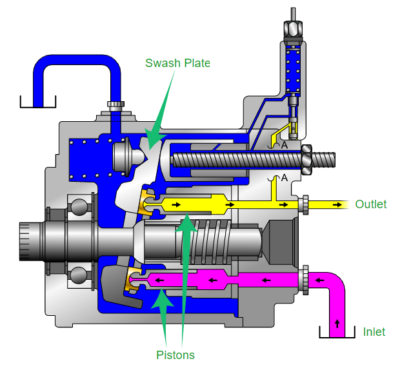
Piston Pump
Piston pumps are categorized into three types: swash plate type pumps, axial piston type pumps, and radial piston type pumps. Essentially, a piston pump consists of pistons moving inside cylinders.
The motion of the pistons displaces hydraulic oil, causing it to flow through the hydraulic system.Piston pumps are capable of handling large flows even under high hydraulic system pressures.
Common applications of piston pumps include marine auxiliary power, machine tools, mobile and construction equipment, metal forming, and oilfield machinery.
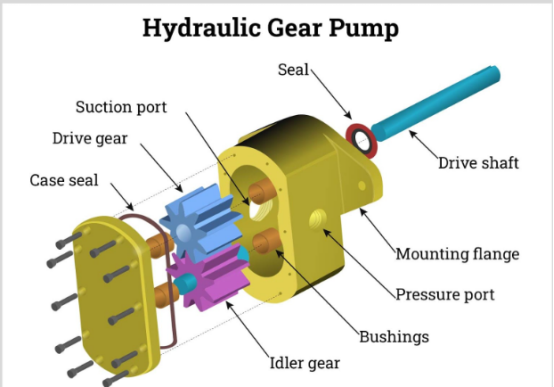
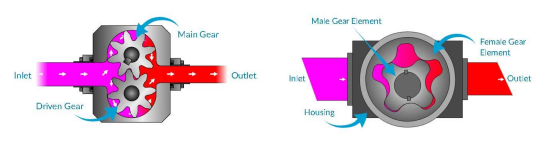
Gear Pump
Gear pumps are divided into “internal gear pumps” and “external gear pumps.”
In a gear pump, one gear is connected to the drive shaft, which meshes with another gear, causing both gears to rotate synchronously.An external gear pump uses two externally meshing spur gears. As the gears rotate in opposite directions side by side, they carry fluid from the low-pressure side to the high-pressure side.An internal gear pump uses an external spur gear and an internal spur gear, with one gear rotating inside the other in the same direction.
Applications of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps, due to their versatility, powerful output, and high efficiency, hold an irreplaceable position in modern industry and everyday life.They are not just the “power source” that provides hydraulic energy, but also the core components that keep various machines and equipment running.Almost every field that requires stable power and heavy load transmission relies on hydraulic pumps.Common applications include:
Construction and Mining
In construction machinery and mining equipment, hydraulic pumps are the key driving and control force.
For example, excavators rely on hydraulic pumps to drive the boom and bucket for digging and loading; loaders use hydraulic systems to lift and dump materials; drilling rigs depend on hydraulic pumps to deliver stable power, ensuring drilling depth and efficiency.
Hydraulic pumps not only ensure smooth equipment operation but also improve precision and construction efficiency.
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial production lines, hydraulic pumps are widely used in molding, injection molding, stamping, bending, and material handling processes.Whether for power input to small machines or continuous operation of large production equipment, hydraulic pumps provide stable flow and pressure support.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, hydraulic pumps are mainly used in hydraulic power steering systems and hydraulic braking systems.
For instance, a hydraulic power steering pump provides additional power when the driver turns the steering wheel, helping vehicles steer more easily under low speed or heavy load conditions.Some commercial and special-purpose vehicles also use hydraulic pumps to drive auxiliary devices, enhancing overall operability and safety.

Factors Affecting the Performance of Hydraulic Pumps
The performance of a hydraulic pump is not only determined by its design and manufacturing process but also influenced by various external and operating conditions.The following key factors directly determine whether the hydraulic pumps can operate stably and efficiently over the long term:
1.Maintenance and Upkeep
Even the highest-quality hydraulic pump cannot maintain good performance without proper maintenance.Cleaning filters in time and checking for internal wear in the pump helps extend equipment lifespan.Regularly replacing hydraulic oil prevents degradation over time and avoids contamination that can cause pump wear.Inspecting and replacing seals effectively.Good maintenance not only improves pump efficiency but also reduces failure rates and lowers overall operating costs. prevents internal and external leakage, maintaining system pressure stability.
2.Operating Temperature
Hydraulic pumps are highly sensitive to temperature.When the temperature is too high, hydraulic oil thins, lubrication performance decreases, seals tend to age, harden, or fail, leading to leakage and reduced efficiency.When the temperature is too low, fluid viscosity rises, flow becomes poor, the pump faces excessive load at startup, and pump wear or damage is more likely.An ideal hydraulic system should be equipped with temperature control devices, such as coolers or heaters, to ensure the pump operates within the recommended temperature range, maintaining optimal efficiency and service life.
3.Pump Speed
The operating speed of a hydraulic pump has a significant impact on its performance.At excessively high speeds, fluid may not fill the pump chamber in time, causing cavitation, noise, vibration, and potential pump damage.At very low speeds, flow becomes insufficient, system output power decreases, and the requirements of actuators may not be met.Therefore, during design and operation, pumps must run within their rated speed range, and frequent rapid acceleration or deceleration should be avoided to reduce stress on mechanical components.
4.Hydraulic Oil Viscosity
The working medium in hydraulic systems is usually hydraulic oil, and its viscosity is one of the primary factors determining pump performance.If the viscosity is too low (the fluid is too thin), the oil film cannot form properly, friction between metal parts increases, internal leakage rises, efficiency drops, and in severe cases, premature wear of components may occur.If the viscosity is too high (the fluid is too thick), flow resistance increases, pump start-up becomes difficult, energy losses rise, operating temperature increases, leading to overheating, and long-term operation may damage the hydraulic pump shaft and seals.
Therefore, when selecting hydraulic oil, it must fall within the viscosity range recommended by the equipment manufacturer, and the fluid condition should be checked regularly.

How do you select hydraulic pumps?
Selecting the right hydraulic pump depends on multiple factors, such as the required flow rate, pressure demands, fluid viscosity, and system efficiency considerations.Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
1.Understand Your Requirements
You need to have clear requirements for your hydraulic system, including flow rate, pressure range, temperature limits, and fluid viscosity.Also consider factors such as space constraints, working environment, and any special features or functions required.
2. Identify the Type of Pump
Based on your system requirements and budget, determine the most suitable pump type (gear pump, vane pump, or piston pump).
3. Calculate Flow Rate and Pressure
Having this information will help you select a pump that best matches your performance needs. If you require professional assistance, you can consult our expert team.
4. Ensure Proper Sizing
Ensure that the physical dimensions of the pump match the space constraints of your system.When selecting a pump, consider installation options, inlet/outlet port sizes, and overall footprint.
5. Check Compatibility
Verify the compatibility between the hydraulic pump and the hydraulic fluid being used.
6. Seek Expert Advice
If you are uncertain about the required information, you can consult relevant experts or reputable suppliers and make choices based on their advice.
Key Factors Affecting the Cost of Hydraulic Pumps
Materials and Manufacturing Process
High-end materials (such as stainless steel or special alloys) and complex manufacturing processes increase the cost, but they enhance durability and reduce maintenance expenses.

Pump Capacity and Performance Specifications
Pumps with higher flow rates and pressure capacities are generally more expensive.For example:
A heavy-duty piston pump: up to 6000 psi and flow rates of 200 gpm, costs significantly more than a light-duty gear pump (up to 3000 psi and 60 gpm).
Brand and Quality
Well-known brands (such as Blince Hydraulic) usually offer reliable designs and good after-sales service.With over 20 years of R&D experience and ISO 9001 and CE certifications, they have established a solid reputation in the global market.Their gear pumps, orbital motors, and piston pumps are known for their high cost-effectiveness and flexible customization capabilities, making them suitable for customers who seek stable performance while also focusing on cost control.
Additional Features
Additional features such as variable displacement, built-in safety mechanisms, or energy-saving designs can raise the price but improve efficiency and reduce maintenance needs.
Cost Evaluation of Hydraulic Pumps
Gear Pumps (Most Economical Type)
Price Range: Approximately $100–$2,000.
Features: Gear pumps, with their simple structure and mature manufacturing process, are considered one of the most cost-effective hydraulic pumps on the market.
They perform reliably in low- to medium-pressure applications (generally below 3000 psi), but due to higher internal leakage and faster wear, they usually require more frequent maintenance.
Piston Pumps (High-End Type)
Price Range: Approximately $500–$5,000, with some high-pressure, high-flow piston pumps exceeding $8,000. Features: Piston pumps are among the most efficient and high-pressure-resistant hydraulic pumps, typically handling pressures up to 6000 psi, making them suitable for heavy-load and high-intensity applications.
Although more expensive, they are widely used in demanding fields such as aerospace, marine, and construction machinery.
Vane Pumps (Mid-Range Type)
Price Range: Approximately $200–$3,000.
Features: Vane pumps excel in noise control and medium-pressure applications. They operate smoothly, are more efficient than gear pumps, but cannot handle as high pressures as piston pumps.
They are commonly used in machine tools, injection molding machines, and light industrial equipment.
Cost Cases in Different Applications
Industrial manufacturing scenarios: Hydraulic pumps cost around $1,000–$3,000.
Small equipment (such as hydraulic presses or small farm tractors): Prices are only $100–$500.
Marine and offshore equipment: Prices range from $3,000–$5,000.
The differences in application scenarios result in significant cost variations.
Maintenance and Impact on Total Cost
The total cost of a hydraulic pump includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance and repair costs.Low-priced pumps that fail frequently can end up being more expensive than high-quality, long-lasting pumps.
How to Evaluate the Total Cost of a Hydraulic Pump?
When purchasing a hydraulic pump, focusing solely on its initial price is far from sufficient.
A comprehensive cost evaluation should include:
Purchase Cost: The initial purchase price, influenced by brand, model, and features.
Operating Cost: Energy consumption during long-term operation.
Maintenance Cost: Expenses for regularly replacing hydraulic oil, seals, etc.
Repair Cost: Potential expenses for breakdown repairs.
High-quality hydraulic pumps may have a higher initial investment, but they offer durability, lower energy consumption, and reduced failure rates, which effectively lower long-term operating and maintenance costs.In contrast, cheaper but lower-quality pumps may result in frequent downtime and high repair costs, ultimately making the total cost higher.

This guide is intended to help you better understand the cost structure of hydraulic pumps and make the most suitable and informed choice for your needs.
Blince Team
Blince Hydraulic is an industry-leading company specializing in complete hydraulic solutions. With over 20 years of experience and long-term cooperation with more than 5,000 global customers, we focus on high-performance hydraulic motors, hydraulic pumps, steering control units, directional valves, hydraulic cylinders, hoses, fittings, and other one-stop hydraulic system solutions.
Our factory group is equipped with advanced CNC machining centers, automated production lines, and precision testing equipment. Certified with ISO9001, CE, SGS, and UL, Blince provides fast, efficient, and high-quality hydraulic solutions to customers in more than 100 countries worldwide. Whether you need small batch customization or large-scale production, we can meet your demands with reliable delivery and competitive performance.
Choose Blince technology — it means efficiency, durability, and professionalism in every hydraulic product we deliver.
To learn more, visit our website: www.blince.com
Tel: +86 180 3845 8522
Email: sales01@blince.com
Website: https://www.blince.com


































