In the world of hydraulics, gear pumps are essential components renowned for their reliability and efficiency. Among the most commonly used types are the internal gear pump and the external gear pump, each with unique advantages, limitations, and ideal applications. Choosing the right one for your system requires a thorough understanding of how they work and what they’re best suited for.
How Does an Internal Gear Pump Work?
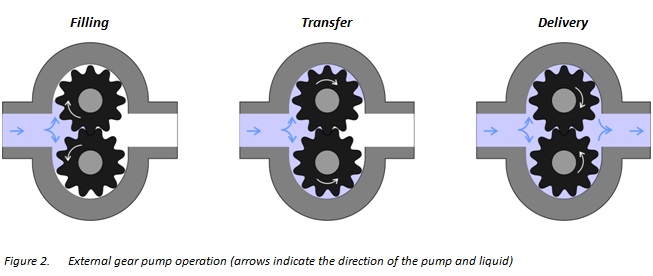
The operation cycle of an internal gear pump consists of three main stages: filling, transfer, and discharge.
When the gears on the inlet side disengage, they create an expanding cavity. Fluid enters this space and is trapped between the gear teeth as they rotate inside the pump casing. The fluid is then transported around the casing to the outlet side. As the gears re-engage on the outlet side, the cavity shrinks and the fluid is pushed out under pressure.
Tight tolerances between the gears and housing allow the pump to generate strong suction at the inlet and minimize backflow from the outlet, though low-viscosity fluids are more prone to leakage.
Limitations of Internal Gear Pumps
Self-Priming with Caveats: Internal gear pumps are self-priming but work best when wetted with the pumped liquid. They should not be run dry for extended periods.
Wear Sensitivity: Due to tight tolerances, internal gear pumps can wear out quickly when handling abrasive fluids or liquids with suspended solids.
Speed and Temperature Considerations: Operating at too low speeds or outside the rated temperature range can affect volumetric efficiency and accelerate wear due to thermal expansion of internal components.
Backpressure Risks: If downstream blockage occurs, the pump continues generating pressure, potentially damaging the system. Pressure relief valves are strongly recommended.
Volumetric Efficiency Decline: Over time, gear wear increases internal leakage, reducing flow rate accuracy and pump performance.
Despite these factors, internal gear pumps offer low-shear handling and are ideal for shear-sensitive fluids such as paints, soaps, and food-grade liquids. Their simple design also makes them easy to disassemble and clean—perfect for sanitary applications.
Internal Gear Pumps: Precision and Smooth Operation
Internal gear pumps consist of a driving gear (rotor) and an idler gear that mesh internally. This compact, low-noise design allows them to handle high-viscosity and low-viscosity fluids alike with excellent self-priming capability.
Key Advantages:
Excellent metering accuracy with minimal pulsation
Efficient handling of viscous liquids
Ideal for hydraulic systems, chemical processing, food, and pharmaceutical dosing
However, they are not suitable for highly abrasive or corrosive fluids, and may operate less efficiently with very thin liquids.
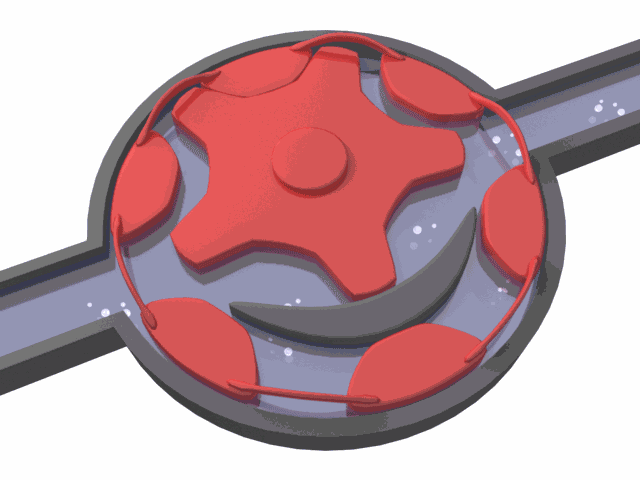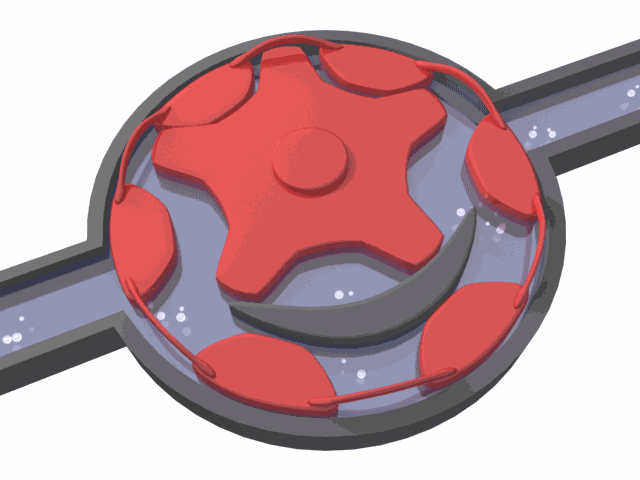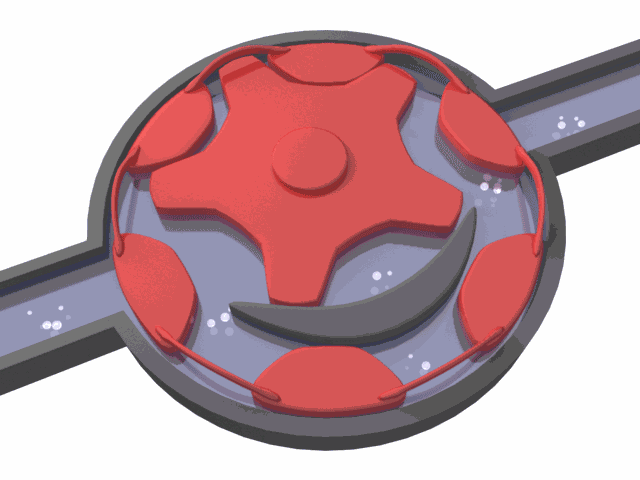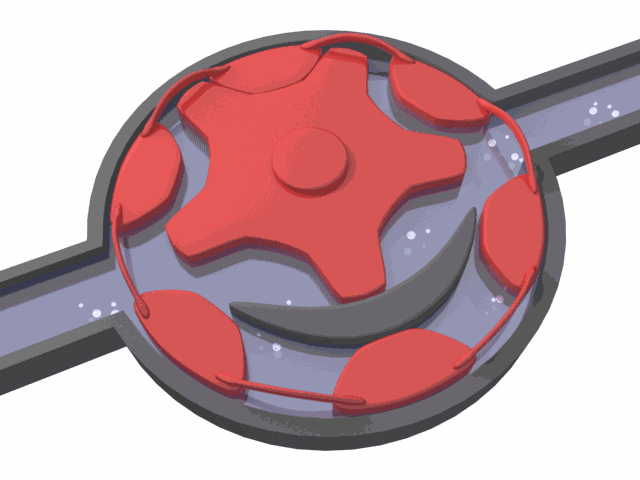
Like internal gear pumps, external gear pumps also go through a filling, transfer, and discharge cycle.
When the gears separate on the inlet side, they create a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump. The liquid is trapped between the gear teeth and the pump housing and is then carried to the outlet side. As the gears mesh again, the cavity shrinks, and the fluid is discharged under pressure. The tight clearance between the gears and casing prevents leakage and ensures suction.
External gear pumps may use spur gears, helical gears, or herringbone gears:
Helical and herringbone gears reduce noise and vibration due to gradual engagement.
Spur gears are easier to manufacture and support higher speeds.
Herringbone designs cancel axial forces, increasing durability and performance.
External Gear Pumps: Rugged and Versatile
External gear pumps are built with two externally meshed gears, one driving and one driven. The fluid is transferred between the teeth and housing.
Key Benefits:
Suitable for a wide variety of fluids, including solvents, corrosive chemicals, and fuel
Withstand high operating pressures up to 500 bar (7250 psi)
Capable of high rotational speeds (up to 3500 rpm or higher)
Strong in lubrication systems, hydraulic power, and industrial applications
Popular in agricultural machinery, mobile equipment, and engine-driven power systems
Modern external gear pumps made from stainless steel or advanced alloys can handle aggressive media like sulfuric acid, sodium hypochlorite, ferric chloride, and sodium hydroxide.
External Gear Pump Limitations
Less efficient with high-viscosity fluids compared to internal gear pumps
Limited self-priming ability when dealing with low-viscosity liquids
Higher pulsation due to external gear meshing
Despite these drawbacks, external gear pumps are favored for their robust structure, ease of maintenance, and cost-efficiency in general-purpose hydraulic applications.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Gear Pump for Your System
Both internal and external gear pumps have their place in industrial hydraulics:
Pump Type | Best For | Key Strengths |
Internal Gear Pump | Viscous, shear-sensitive, hygienic applications | Precise dosing, smooth flow, quiet |
External Gear Pump | General industrial and hydraulic applications | High pressure, rugged, wide fluid compatibility |
Selection Tips:
Evaluate the viscosity and abrasiveness of the fluid
Consider the required flow rate, pressure, and system layout
Match pump materials to fluid chemistry and operating temperature
Use proper filtration and pressure relief valves to enhance life span
By understanding how each pump type works and where it excels, you can make an informed choice that ensures efficiency, longevity, and cost-effectiveness in your hydraulic system.



















